With the ongoing digitalization, an ever-increasing part of the value chain is shifting to the Internet. As a result, more data can be found online.
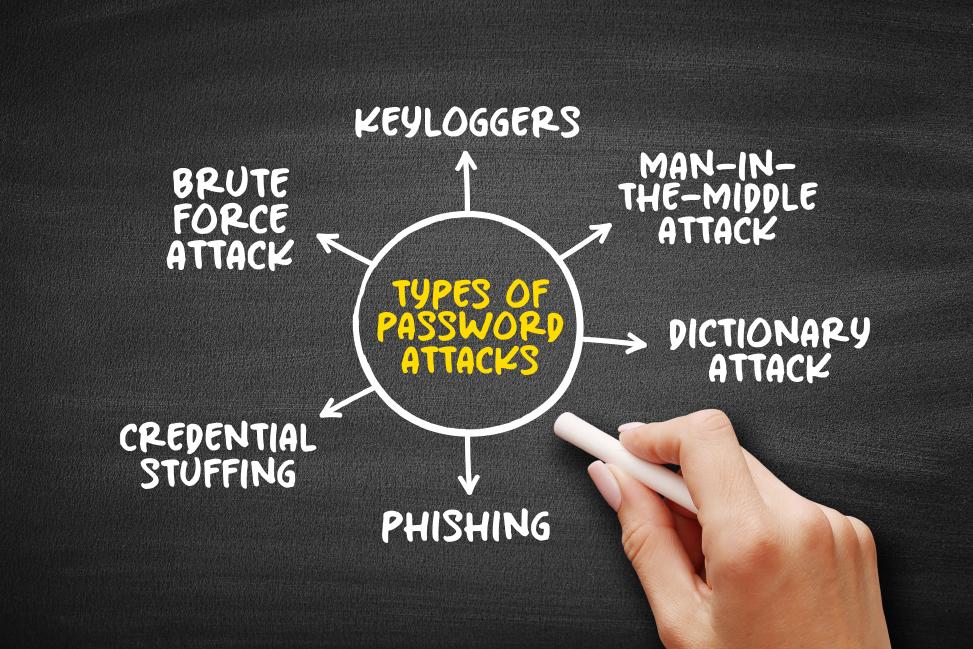
Attackers are also trying to profit from the growing importance of data available online and are increasingly posing a threat to everyone involved. Using various attack methods such as brute force attacks, dictionary or password spraying attacks, phishing, man-in-the-middle attacks, keyloggers, credential stuffing, and brushing scams, they attempt to exploit technological vulnerabilities in database or application access or poorly chosen user access data in order to steal identities or gain financial advantage. This situation signifies a progressively escalating risk for both users and portal operators, particularly given that the potential consequences can often be devastating.
In the following article, we highlight how portal operators and users can best protect themselves against hacker attacks on the Internet and how they can make it as difficult as possible for attackers to even become the focus of a hacker. And it’s not that complicated. Read on to find out how strong and secure passwords, regular software updates, and implementing certain technical precautions is crucial and can greatly diminish the chances of falling victim to hacking. After all, caution, security awareness, and prevention are the best protection against potential cyberattacks.
What Does a Hacker Hope to Achieve by Attacking My User Account?
With the increasing digitization of our working and private lives, digitally stored company and user data, our online access to social media accounts, bank accounts, shopping or entertainment apps, etc., with stored payment data but also cryptocurrencies, are increasingly becoming the gold of the 21st century.
While in earlier centuries robbers first attempted to attack stagecoaches and later targeted banks and ATMs as lucrative targets, the robbers (now known as hackers) of the 21st century focus on our online accounts and access. In today’s digital landscape, it’s crucial to understand that attackers are increasingly targeting third-party systems and user accounts. There can be very different motives for an attack, but they usually all have something to do with the hacker being able to derive some kind of profit from the attack, such as
- Theft of confidential and protected data, often involving industrial espionage
- Installation of malware (malicious software) to damage the attacked infrastructure or spy on third-party systems
- Assumption of foreign identities and use of these to commit “online” crimes such as the fraudulent use of credit card data
- Restricting company access to secure ransom payments for data recovery and company access, also known as ransomware
- Redirection of server traffic
The damage that can be caused by these attacks depends on the type of application that has been hacked and the permissions that the hacked account (user vs. admin account) has. Unfortunately, the global damage caused by online fraud, account takeovers, and data theft is increasing every year. The damage is already estimated to be in the billions globally, and no one (whether portal providers or users) should underestimate this threat in the hope that a hacker attack will only affect others.
With the following information, we would like to help the various parties involved to increase their own level of security, reduce the risk of possible hacker attacks, and thus protect themselves as best as possible.
How Can Access Providers Prevent Hacker Attacks?
It is not only large companies that are targeted by cybercriminals, but also small and medium-sized enterprises. All companies in the digital sector should therefore be aware that even a single successful attack can result in severe consequences, including significant financial losses, complete business failure insolvency, and irreparable damage to their reputation. Consequently, it is essential to establish, develop, and continuously monitor available security mechanisms to ensure the best possible protection in line with the current state of the art. The security of any device, website, application, database, or system is fundamentally reliant on its underlying security architecture. By investing in a robust and well-designed security framework, you can significantly enhance protection against potential threats and vulnerabilities. This foundational aspect is crucial for ensuring the integrity and safety of your digital assets.
The security of a device, website, application, database, or system is fundamentally reliant on the underlying security architecture of the respective operator. When designing their architecture, administrators or developers should ensure that at least the following criteria are met as minimum protection against all types of password attacks:
Secure password assignment
In systems deemed less critical, it is imperative for operators to implement a policy mandating a minimum password length of no fewer than 10 characters. This requirement should include a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters to ensure adequate security measures are upheld. For critical systems, it is imperative that the password comprises a minimum of 12 characters.
In addition, password quality or strength should be further enhanced by a built-in password strength meter when entering passwords as part of the registration or log-in process. Another protective mechanism can be the installation of a “breached password detector,” which ensures that no hacked passwords are used. These two additional security measures make it impossible for users to choose a password that is too weak.
Automatic logout function
The automatic logout function represents one of the most effective, albeit straightforward, security mechanisms, as it significantly limits the possibilities for attack attempts by an attacker, depending on how it is configured. It is therefore even more surprising that only a minority of portal operators use this simple security method.
The access solution detects when a password is entered incorrectly and temporarily blocks the login. Depending on the level of protection used, this should happen after the third, fifth, or at the latest after the tenth attempt. The lockout time, which can be freely selected by the operator, can be 10 seconds after the third incorrect entry, for example, and increase the more incorrect passwords are entered (e.g., one hour after 10 incorrect entries). This largely prevents automated brute force attacks, as the attack slows down and may ultimately no longer be worthwhile. However, caution is advised here as well, as informing users about the lockout function gives hackers unnecessary information.
Salting
Salting adds an extra layer of security. Passwords are not simply hashed; they are first supplemented with a additional random string of characters. This implies that adversaries are required to ascertain not only the password but also the supplementary salt value. Using this salt value mechanism reduces the likelihood of a brute force attack being successful.
Block suspicious IP addresses
One of the most common mechanisms for detecting and actively combating suspicious login attempts is rate limiting. This involves delaying or completely blocking IP addresses from which too many login attempts are made. This indicates that the IP address formerly employed by the attacker is now rendered inoperative, or can only be used to a limited extent, for a certain time.
Use of monitoring software
Even though this measure goes beyond the minimum protection required for an access system, it is still recommended. Monitoring software of this kind enables brute force attacks to be detected early and admins to stay informed about any suspicious activities. They can then initiate further defensive measures, such as tighter network management, to detect further data breaches.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) - Two-factor authentication (2FA)
Even though two-factor authentication or multi-factor authentication exceeds the minimum protection requirements for many applications, it is still essential for critical applications such as bank accounts to further increase protection against intruders. Adding another authentication factor (e.g., an additional code from an authentication app) in addition to password access significantly increases system security. Even guessing a password no longer helps hackers, as the system is protected by an additional factor (2FA/MFA). Classic brute force attacks don’t stand a chance here.
Use of firewalls and antivirus software
Even though firewalls and antivirus programs have been around for a long time, they remain the most crucial initial line of defense against online intruders. They monitor and block incoming and outgoing data traffic and detect and delete harmful virus software or malware before any damage can be done. Most operating systems and browsers already have these security measures built in, at least in a basic version. Nevertheless, regular checks on the effectiveness of these solutions should be carried out.
How Can I Best Protect Myself Against a Hacker Attack?
A strong password is the best protection
By choosing a secure password, we as users can make an important contribution to the security of our user accounts. Where possible, end users should choose a password that consists of at least 10 characters and includes a mix of lowercase and uppercase letters, numbers, and special characters. By doing so, you expand your options to approximately 94 possible characters, resulting in 94^10, which equates to a total of 53,861,511,409,489,970,176 (53 trillion) potential combinations.
It is important to avoid frequently used passwords and not to use simple number sequences (123456, 987654). This also applies to simple letter sequences such as qwerty or abcdef. You should also avoid using simple words or names, as these can be found in many dictionaries and are relatively easy to hack.
- In our blog article “Password Length vs. Password Complexity: Or Should It Be Password Strength?” we discussed the current state of password security in detail.
- In “How to Remember a Strong Password, or: An Exploration of Security in the Digital Age”, we showed you how to remember strong, complex passwords more easily. It is imperative to refrain from recording your passwords on paper or reusing them across multiple websites!
- But password manager can also be extremely helpful, as we have already described in our blog article “Should I Use a Password Manager or the One-Password Solution?”
Two-factor authentication (2FA) for additional security
In addition to choosing the best possible password, you should take advantage of any optional multi-factor authentication (MFA) offered by your access provider. Implementing MFA or 2FA significantly enhances the security of your online accounts by introducing an extra layer of protection for your password. The big advantage here is that even if your password is compromised, hackers will not be able to access your data.
Safe surfing on the Internet
When surfing the Internet, you can lay the foundation for your own online security through your own attention and caution. This includes always making sure that you, as a user, only visit websites with secure connections that are encrypted with SSL and identified by “https://” in the URL and a padlock symbol in the address bar. Data encryption allows you to exchange data securely over the Internet.
In addition to data encryption, you should avoid using public Wi-Fi whenever possible, as hackers can easily intercept data on poorly protected networks. If you cannot avoid using public networks, we recommend using virtual private networks (VPNs), which also encrypt data traffic on Wi-Fi networks.
Finally, you should always be cautious when entering personal data online. In addition, you should take care not to click on suspicious links or pop-up ads from fake websites, as these can lead to fraudulent websites designed to steal personal data (see also the next section).
Caution, spam filters, and antivirus software against phishing
In addition to surfing the Internet safely, it is also essential to observe security measures when handling personal e-mails. By sending trustworthy looking but fake phishing e-mails from a supposedly familiar sender such as a bank, online retailer, or telephone or energy provider, urgent action is requested. When you click on embedded links or attachments, you are often redirected to a counterfeit website and asked to enter sensitive data.
Spam filters and antivirus programs help you protect yourself reliably against phishing.
Nevertheless, you should treat incoming e-mails with the necessary skepticism, especially those that urge you to take urgent action or request sensitive data, so that you do not fall victim to a phishing attack.
For example, you should pay attention to slight deviations in the sender’s address, exercise vigilance regarding potential spelling and grammatical errors, and most importantly, refrain from clicking on links and attachments from unknown senders to protect yourself as best as possible against online threats. Further information on how you can best protect yourself against phishing attacks can be found here.
If you are unsure whether the e-mail was sent by the suggested sender, contact them using an alternative method, such as an online chat service or a phone number, rather than using the contact details provided in the e-mail. This will help you avoid becoming a victim of a phishing attack.
Software updates are essential
Furthermore, you should ensure that the operating system software of all devices used (e.g., computers, smartphones, tablets) is updated regularly and kept up to date. This is a fundamental component of your own cybersecurity. This is even more important because updates not only contain new features but also fix known vulnerabilities in the software with security patches. To make it easier for us users, most providers now offer automatic update routines. You should take advantage of this option, as it ensures that your system is optimally always protected without any action on your part.
In addition to the system updates, you should also regularly update other devices such as routers or IoT devices, as well as all applications you have installed, so that they do not leave any points of attack open to hackers.
What Should I Do If I Am Hacked?
All of the above preventive measures should be followed carefully, even though the best security measures cannot guarantee 100% protection. If you do become the victim of a cyber-attack, it is important to remain calm and act immediately.
Lock up all affected accounts or change any passwords that may have been compromised. If you are an employee of a company, contact your company’s IT support immediately so that your IT department can investigate the incident and take appropriate countermeasures as quickly as possible. At the same time, your IT administrators will attempt to close the security gap as quickly as possible and remove any malware from the affected systems, such as your computer or online account.
Regardless of whether the incident occurred in your private or business life, document the incident as thoroughly as possible, take screenshots of any unusual screen displays, and do not destroy any information. This not only helps IT specialists to repair the damage but is also often essential for possible (criminal) reports to the police or other supervisory authorities such as the state data protection officer, which is often mandatory, at least in the business sector.
It is advisable to diligently monitor your accounts for any suspicious activity and to regularly review your credit card statements so that you can identify any unauthorized charges as quickly as possible.
Conclusion: Protect Yourself Proactively Against Online Threats
Due to the ongoing digitalization of our society, cyberattacks are becoming increasingly attractive to hackers as a means of making money. For us as users, this means that proactive action and the best possible implementation of protective measures are becoming increasingly essential for our own protection. By following the security measures mentioned above, such as using strong passwords and 2FA/MFA and only visiting encrypted websites, we can effectively defend ourselves against cybercriminals with simple measures. The necessary caution when dealing with potentially fake e-mails and the use of spam filters and antivirus software, is imperative in substantially mitigating the risks associated with phishing attacks.
Consequently, it is a must do to remain informed about the latest security developments, and implement recommended protective measures to reduce the risk of becoming a victim of a hacker attack as far as possible.